Quoting Robin Sloan
A reflection on the arrival of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), arguing that its 'general' nature distinguishes it from previous purpose-built AI models.

A reflection on the arrival of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), arguing that its 'general' nature distinguishes it from previous purpose-built AI models.
A reflection on the arrival of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), arguing that its 'general' nature distinguishes it from all previous purpose-built AI models.
Explores how AI language models shift a programmer's role from writing code to managing context and providing detailed specifications.

Analyzes LLM APIs as a distributed state synchronization problem, critiquing their abstraction and proposing a mental model based on token and cache state.

Explores training a hybrid LLM-recommender system using Semantic IDs for steerable, explainable recommendations.

A Chrome engineer discusses the design challenges and considerations for creating new built-in AI web APIs, focusing on the prompt API and task-based models.

Critique of the 'how many r's in strawberry' test as a poor benchmark for AI intelligence, arguing it measures irrelevant trivia.
Explores how advanced AIs use 'chains of thought' reasoning to break complex problems into simpler steps, improving accuracy and performance.
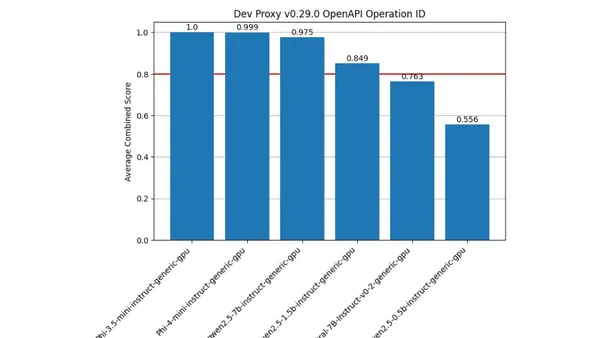
A guide to benchmarking language models using a Jupyter Notebook that supports any OpenAI-compatible API, including Ollama and Foundry Local.

Explains why standard language model benchmarks are insufficient and how to build custom benchmarks for specific application needs.

A tutorial on building a transformer-based language model in R from scratch, covering tokenization, self-attention, and text generation.
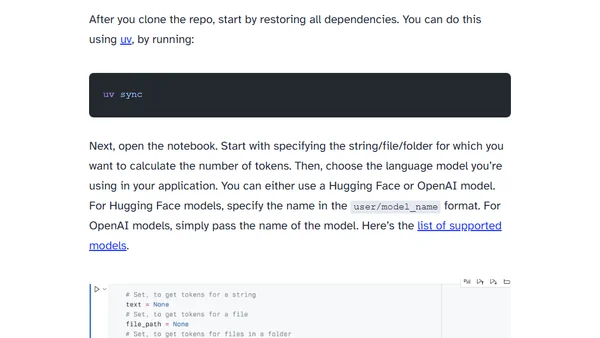
Learn how to accurately calculate token counts for strings using language models with a provided Jupyter Notebook tool.
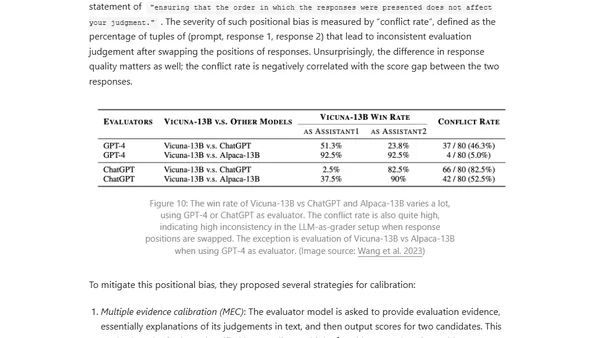
Explores reward hacking in reinforcement learning, where AI agents exploit reward function flaws, and its critical impact on RLHF and language model alignment.

A philosophical and technical exploration of how Large Language Models (LLMs) transform 'next token prediction' into meaningful answer generation.

Analyzes the latest pre-training and post-training methodologies used in state-of-the-art LLMs like Qwen 2, Apple's models, Gemma 2, and Llama 3.1.

The article distinguishes between interactive and transactional prompting, arguing that prompt engineering is most valuable for transactional, objective tasks with LLMs.

Explores the difference between rigorous prompt engineering and amateur 'blind prompting' for language models, advocating for a systematic, test-driven approach.
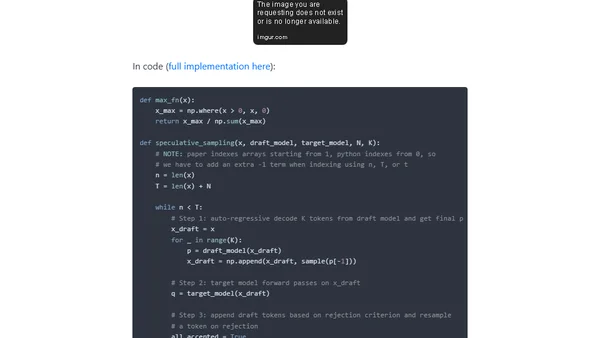
Explains speculative sampling, a technique using a draft and target model to accelerate large language model text generation.
A guide to implementing few-shot learning using the GPT-Neo language model and Hugging Face's inference API for NLP tasks.
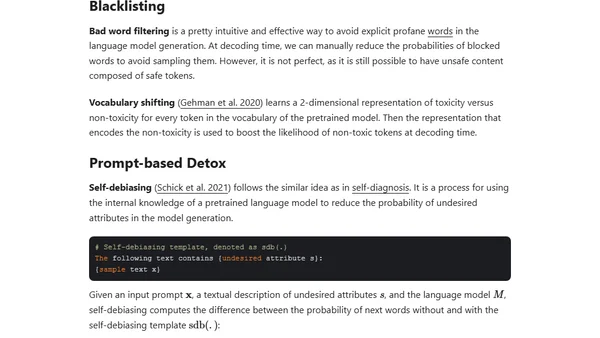
Explores the challenge of defining and reducing toxic content in large language models, discussing categorization and safety methods.