
Why We Think
Explores how increasing 'thinking time' and Chain-of-Thought reasoning improves AI model performance, drawing parallels to human psychology.
Lilian Weng is a machine learning researcher documenting deep, well-researched learning notes on large language models, reinforcement learning, and generative AI. Her blog offers clear, structured insights into model reasoning, alignment, hallucinations, and modern ML systems.
50 articles from this blog

Explores how increasing 'thinking time' and Chain-of-Thought reasoning improves AI model performance, drawing parallels to human psychology.
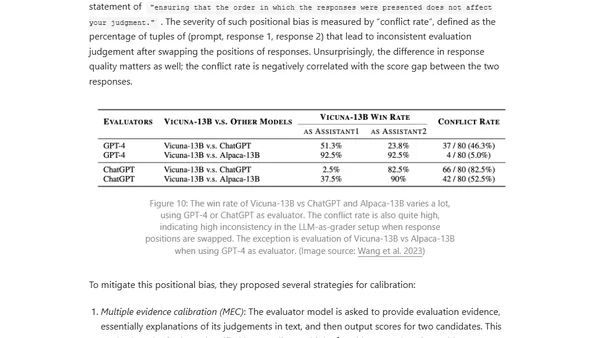
Explores reward hacking in reinforcement learning, where AI agents exploit reward function flaws, and its critical impact on RLHF and language model alignment.

Explores the causes and types of hallucinations in large language models, focusing on extrinsic hallucinations and how training data affects factual accuracy.
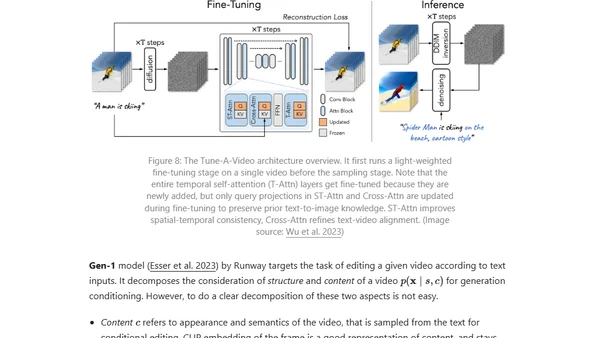
Explores the application of diffusion models to video generation, covering technical challenges, parameterization, and sampling methods.

Explores the importance of high-quality human-annotated data for training AI models, covering task design, rater selection, and the wisdom of the crowd.
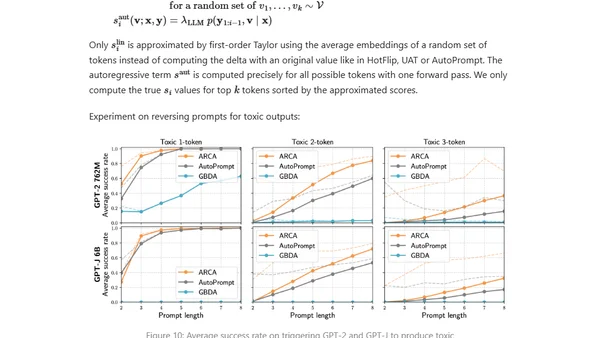
Explores adversarial attacks and jailbreak prompts that can make large language models produce unsafe or undesired outputs, bypassing safety measures.

An overview of LLM-powered autonomous agents, covering their core components like planning, memory, and tool use for complex problem-solving.

An overview of prompt engineering techniques for large language models, including zero-shot and few-shot learning methods.

An updated, comprehensive overview of the Transformer architecture and its many recent improvements, including detailed notation and attention mechanisms.

Explores techniques to optimize inference speed and memory usage for large transformer models, including distillation, pruning, and quantization.

A deep dive into the Neural Tangent Kernel (NTK) theory, explaining the math behind why wide neural networks converge during gradient descent training.
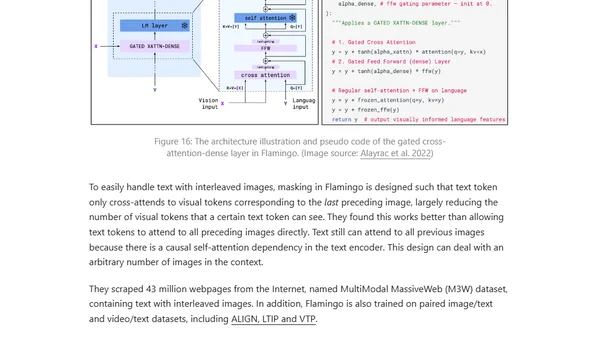
Explores methods for extending pre-trained language models to process visual information, focusing on four approaches for vision-language tasks.
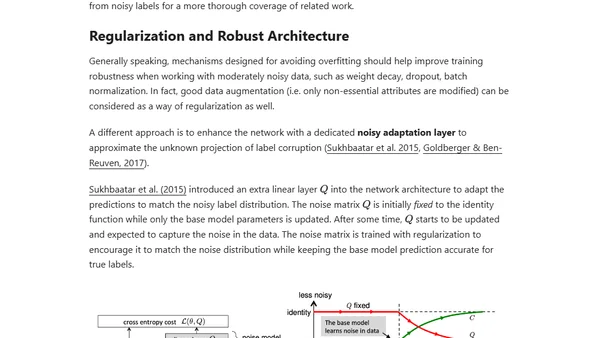
Explores synthetic data generation methods like augmentation and pretrained models to overcome limited training data in machine learning.
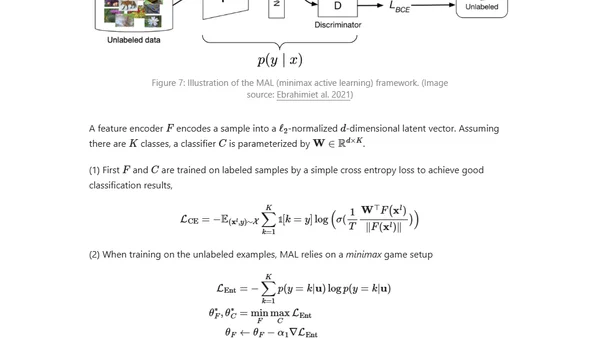
Explores active learning strategies for selecting the most valuable data to label when working with a limited labeling budget in machine learning.

Explores semi-supervised learning techniques for training models when labeled data is scarce, focusing on combining labeled and unlabeled data.
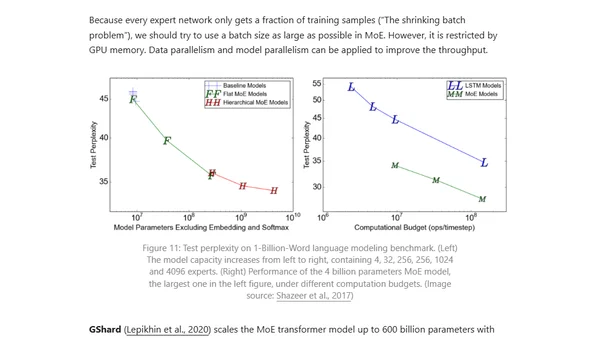
Explores parallelism techniques and memory optimization strategies for training massive neural networks across multiple GPUs.
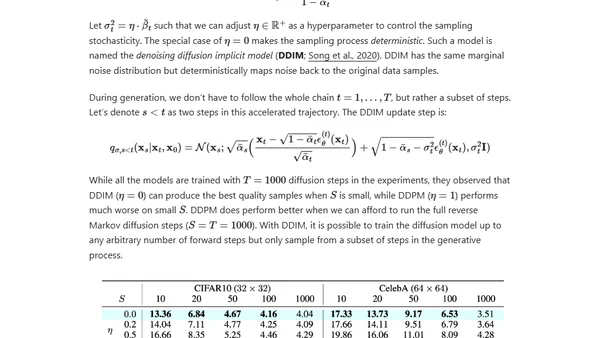
An in-depth technical explanation of diffusion models, a class of generative AI models that create data by reversing a noise-adding process.
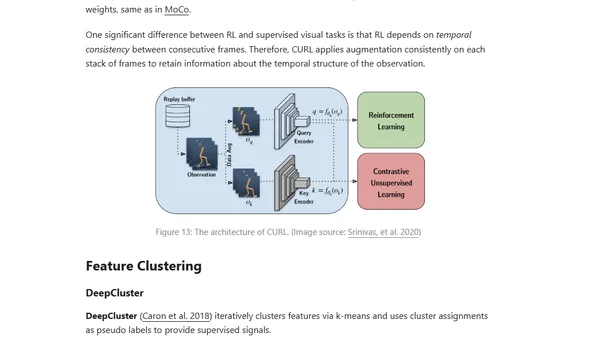
Explains contrastive representation learning, its objectives like contrastive and triplet loss, and its use in supervised and unsupervised machine learning.
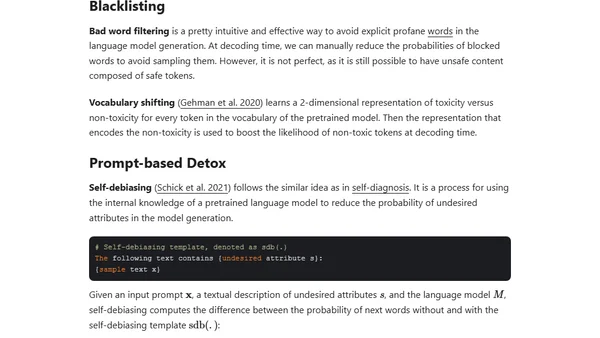
Explores the challenge of defining and reducing toxic content in large language models, discussing categorization and safety methods.

Explores methods for controlling attributes like topic and style in neural text generation using decoding strategies, prompt design, and fine-tuning.