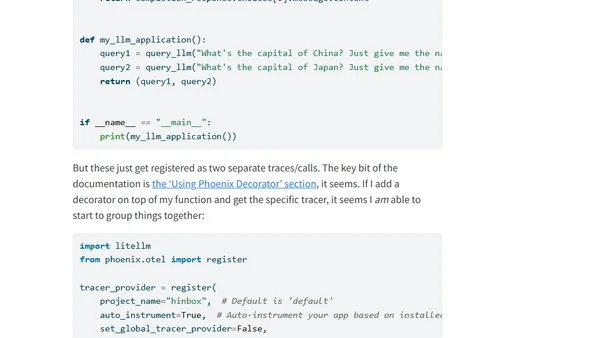
Trying to instrument an agentic app with Arize Phoenix and litellm
A technical guide on instrumenting AI agentic applications using Arize Phoenix and litellm for observability and trace grouping.
Alex Strick van Linschoten is ML Engineer bij ZenML en deelt zijn technische inzichten over machine learning, realtime infrastructuur, Python, Ruby, JavaScript, Go, AWS en open-source projecten zoals Ekko en Gemini by Example.

20 articles from this blog

A technical guide on instrumenting AI agentic applications using Arize Phoenix and litellm for observability and trace grouping.
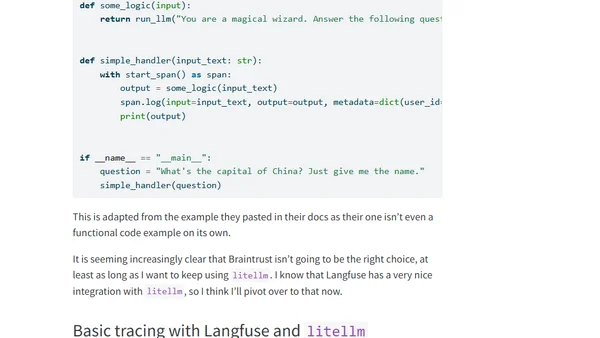
A developer's technical walkthrough of instrumenting LLM tracing for litellm using Braintrust and Langfuse, detailing setup and challenges.
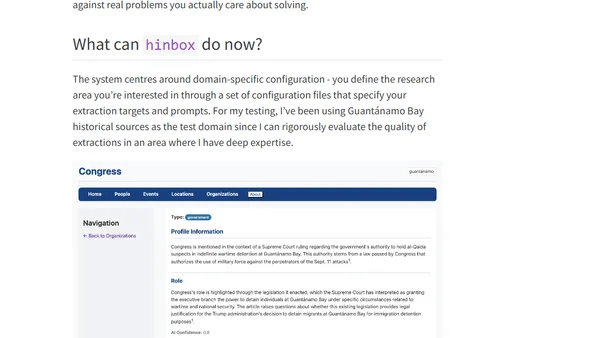
Introducing hinbox, an AI-powered tool for extracting and organizing entities from historical documents to build structured research databases.

A summary of a practical session on analyzing and improving LLM applications by identifying failure modes through data clustering and iterative testing.

A blog post summarizing key concepts from an AI Evals course, focusing on mental models like the 'Three Gulfs' for improving LLM applications.
A hands-on review of Google's updated Gemini Deep Research tool with the 2.5 Pro model, covering its features, usability, and areas for improvement.
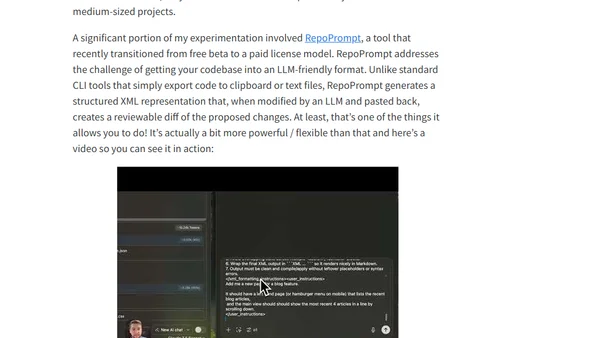
A developer shares insights and practical tips from a week of experimenting with local LLMs, including model recommendations and iterative improvement patterns.
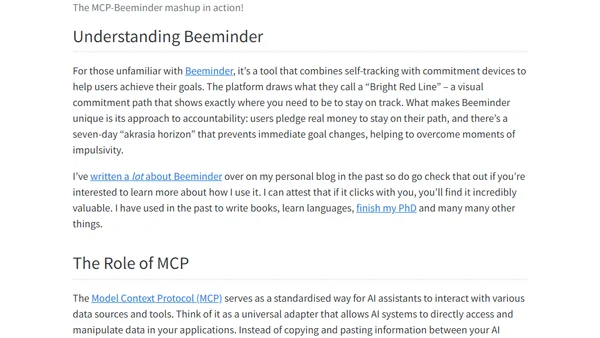
A developer builds an MCP server to connect AI assistants like Claude to Beeminder, a personal goal-tracking app, enabling direct data interaction.

Introducing Tinbox, an LLM-based tool designed to translate sensitive historical documents that standard models often refuse to process.

Reflections on the first unit of the Hugging Face Agents course, focusing on the potential and risks of code agents and their evaluation.
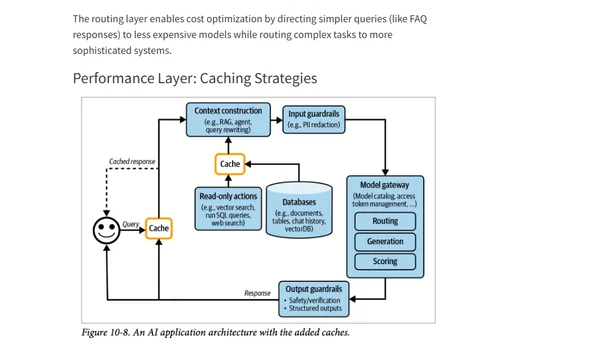
Explores AI engineering architecture patterns and user feedback methods, from simple APIs to complex agent-based systems.
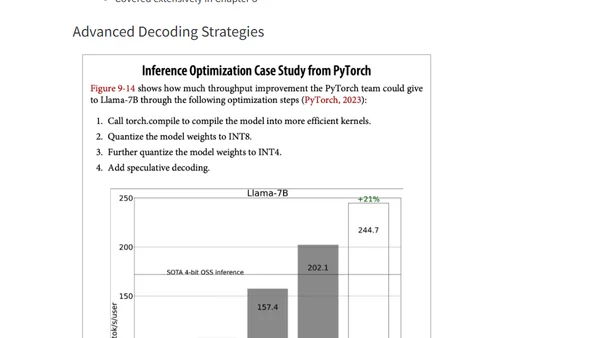
Summary of key concepts for optimizing AI inference performance, covering bottlenecks, metrics, and deployment patterns from Chip Huyen's book.

Notes on dataset engineering from Chip Huyen's 'AI Engineering', covering data curation, quality, coverage, quantity, and acquisition for AI models.

A summary of Chip Huyen's chapter on AI fine-tuning, arguing it's a last resort after prompt engineering and RAG, detailing its technical and organizational complexities.
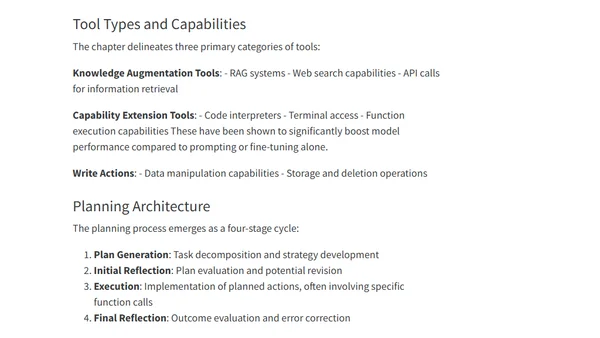
Analysis of Chapter 6 from Chip Huyen's 'AI Engineering' book, focusing on RAG systems and AI agents, their architecture, costs, and relationship.

Analysis of Chip Huyen's chapter on AI system evaluation, covering evaluation-driven development, criteria, and practical implementation.

Summarizes key challenges and methods for evaluating open-ended responses from large language models and foundation models, based on Chip Huyen's book.

A summary and discussion of Chapter 1 of Chip Huyen's book, exploring the definition of AI Engineering, its distinction from ML, and the AI Engineering stack.

Final notes from a book on LLM prompt engineering, covering evaluation frameworks, offline/online testing, and LLM-as-judge techniques.

A summary of Chapter 6 from 'Prompt Engineering for LLMs', covering prompt structure, document templates, and strategies for effective context inclusion.