Physica: The Physics World Model for Scientific AI
Introducing Physica, a Physics World Model AI that enforces physical laws to prevent errors in AI-generated simulations, moving beyond token fluency.

Introducing Physica, a Physics World Model AI that enforces physical laws to prevent errors in AI-generated simulations, moving beyond token fluency.

Highlights ICML 2021 invited talks on applying machine learning to scientific domains like drug discovery, climate science, poverty alleviation, and neuroscience.
A critique of MATLAB's flaws and a nostalgic look at its unique productivity features for scientific computing, with suggestions for improvement.
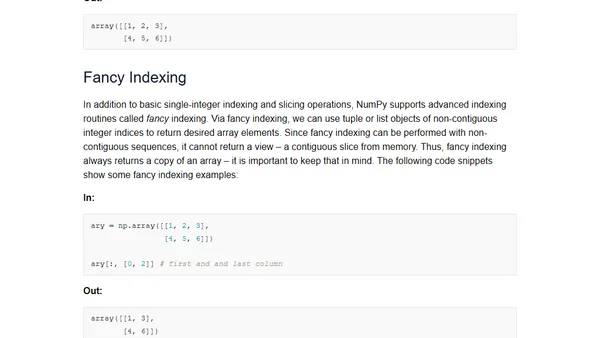
An introduction to scientific computing in Python using NumPy for numerical arrays and Matplotlib for data visualization.
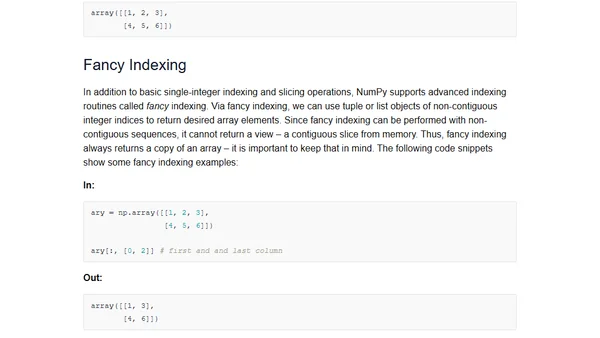
A tutorial on using NumPy for numerical arrays and Matplotlib for data visualization in Python, aimed at scientific computing and machine learning.

Authors of scikit-learn receive a major scientific prize, highlighting a cultural shift towards recognizing open-source software as valuable academic contribution.
Fedora Scientific now offers Vagrant boxes, providing a pre-configured environment for scientific computing with KDE desktop and open-source tools.

An overview of C/C++ libraries for scientific computing, including the GNU Scientific Library (GSL), Blitz++, and the Ch interpreter.
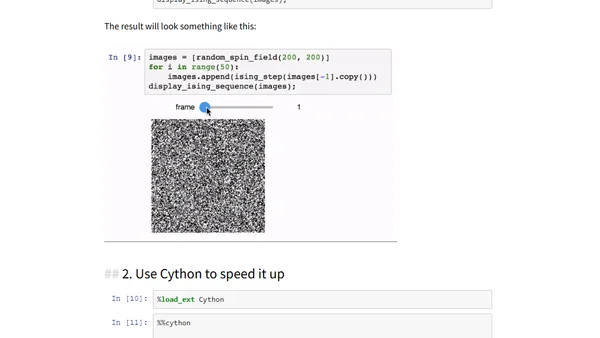
A tutorial on using Cython to optimize slow numerical Python code, demonstrated with an Ising Model simulation.

Argues that scientific progress requires reusable software libraries, not just reproducible results, and discusses challenges in computational research.

Argues that Python is the best programming language for scientists to learn, highlighting its community, learning resources, and scientific packages.

Announcing EuroSciPy 2015, the European conference on Python for scientific computing, with calls for papers, talks, and tutorials.

Explains the Python Buffer Protocol (PEP 3118), showing how objects like arrays and NumPy ndarrays share data efficiently without copying.
A guide to installing Python scientific libraries (NumPy, SciPy, matplotlib) on macOS 10.9, covering both Anaconda/Miniconda and manual pip installation methods.
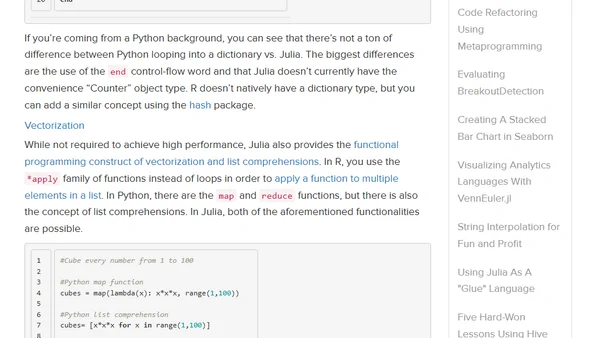
An introduction to the Julia programming language for scientific computing, covering installation, package management, and basic syntax comparisons.

A 2016 article analyzing the slow adoption of Python 3 in the scientific community, now outdated with a recommendation to just use Python 3.

A tutorial on creating an animated optical illusion using Python's Matplotlib library, including code and explanations.

Argues that Python's dominance in scientific computing will endure due to its massive community on GitHub and the complementary role of languages like Julia.
A tribute to John Hunter, creator of the matplotlib Python library, reflecting on his impact on scientific computing and open source.
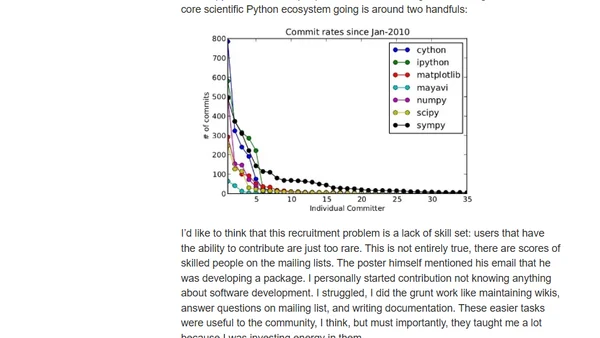
A developer discusses the challenges of open-source maintenance and urges users to contribute code instead of demanding features.