
Explainable unsupervised query tagging
Explains an unsupervised method for tagging search queries using evidence theory and Python, demonstrated with map query examples.
SEO Short Description (2–3 lines): Emir U. is a research-focused software engineer applying mathematics, statistics, and computer science to real-world problems, with 18+ years in software and 7+ years in commercial research. A PhD candidate in astronomy with a background in applied maths and philosophy, he writes about machine learning, logic, and statistical modeling.
24 articles from this blog

Explains an unsupervised method for tagging search queries using evidence theory and Python, demonstrated with map query examples.

A statistical analysis of the classic board game Snakes & Ladders, modeling it as a Markov chain to calculate the expected game length.

Introduces pyevidence, a Python library for practical implementation of Dempster-Shafer evidence theory, addressing computational challenges.

Explores using Dempster-Shafer theory to model probabilistic beliefs about sets based on quantified logical statements, as an alternative to Bayesian methods.

A statistical reasoning test with three practical problems on sorting uncertain fractions, highlighting anomalies, and estimating population sizes.

Explains the 'data programming' weak supervision paradigm for training models using noisy heuristic labels, with a practical example.

Using an LLM to label Hacker News titles and train a Ridge regression model for personalized article ranking based on user preferences.

Explains the Kelly criterion for bet sizing and extends it to multiple simultaneous independent bets using mathematical derivation and Python code.

Explains kernel ridge regression and scaling RBF kernels using random Fourier features for efficient large-scale machine learning.

Explores a closed-form solution for linear metric learning, deriving a transformation matrix to align feature distances with response distances.
A developer documents their journey tackling the 'Billion Row Challenge' in Fortran, optimizing performance from over 2 minutes to under 6 seconds.

A developer compares solving Advent of Code puzzles in Prolog, Haskell, Python, and Scala, analyzing productivity, code style, and language ergonomics.

Introduces 'Domicles,' a logic puzzle using domino tiles, with examples and a Prolog implementation for puzzle generation.

A technical exploration of a minimal probabilistic Prolog meta-interpreter for stochastic simulation.

Explores using logic programming (Prolog) for data analysis, demonstrating its application on a diamond pricing dataset to build robust models.
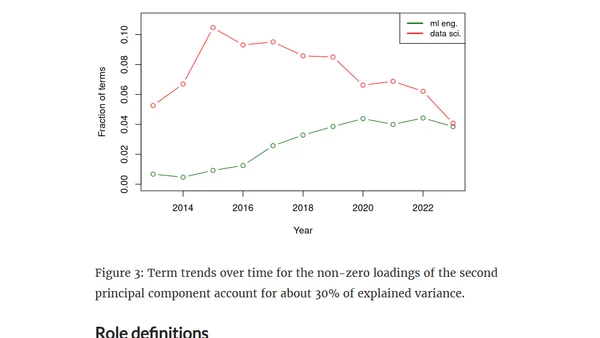
Analysis of Hacker News job posts shows the Data Scientist role declining while ML Engineer roles rise, indicating a shift in the data job market.
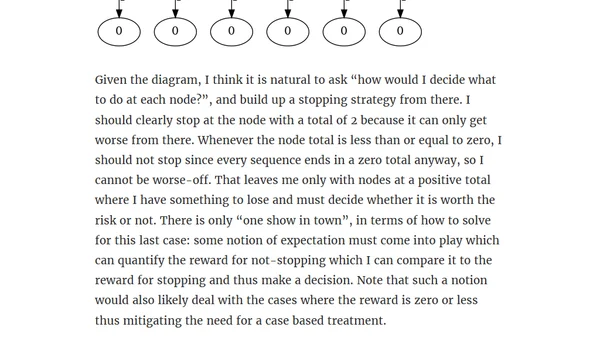
A detailed analysis of an optimal stopping problem involving drawing cards for reward, exploring mathematical strategies and first-principles reasoning.
Explains blocking, covariate adjustment, and optimal design to improve statistical power in online experiments, with a Python implementation.

Explores using logic programming and Prolog for semi-supervised clustering, arguing it's more intuitive than traditional algorithms for rule-based problems.

Explores using Prolog for symbolic reasoning in data science, integrating it with Python for tasks like piecewise regression analysis.