MySQL: Are you actually utilizing your indexes?
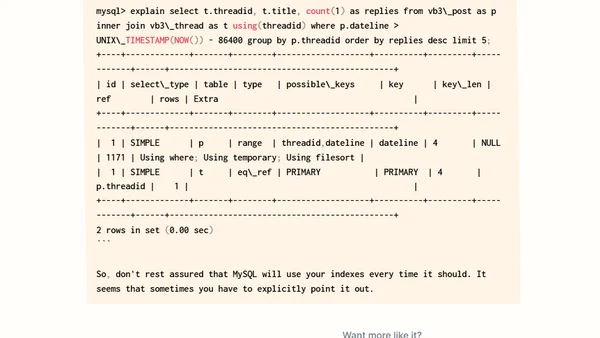
Read OriginalThis technical article demonstrates how subtle differences in MySQL query syntax can dramatically impact performance. By changing a WHERE clause from 'UNIX_TIMESTAMP(NOW()) - post.dateline < 86400' to 'post.dateline > UNIX_TIMESTAMP(NOW()) - 86400', query time dropped from ~10 seconds to 0.03 seconds. The author explains how the second query allows MySQL to properly utilize the B+ tree index on the dateline column, with execution plan analysis using EXPLAIN to show the performance difference.
hozzászólás
No comments yet
Be the first to share your thoughts!
Browser Extension
Get instant access to AllDevBlogs from your browser
Top of the Week
No top articles yet